
Question 1 Back to menu 17 Which of these structures controls cell division? ġ8 Question 2 Back to menu Which of these describes the plant vacuole contents? ġ9 Question 3 Back to menu Structure which controls the entry or exit of substances Ģ0 Question 4 Back to menu Which one of these statements is correct? Ģ0 Question 5 Back to menu Which of the following is a function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum? Ģ0 Question 6 Back to menu Which one of the following is a function of the Golgi body?
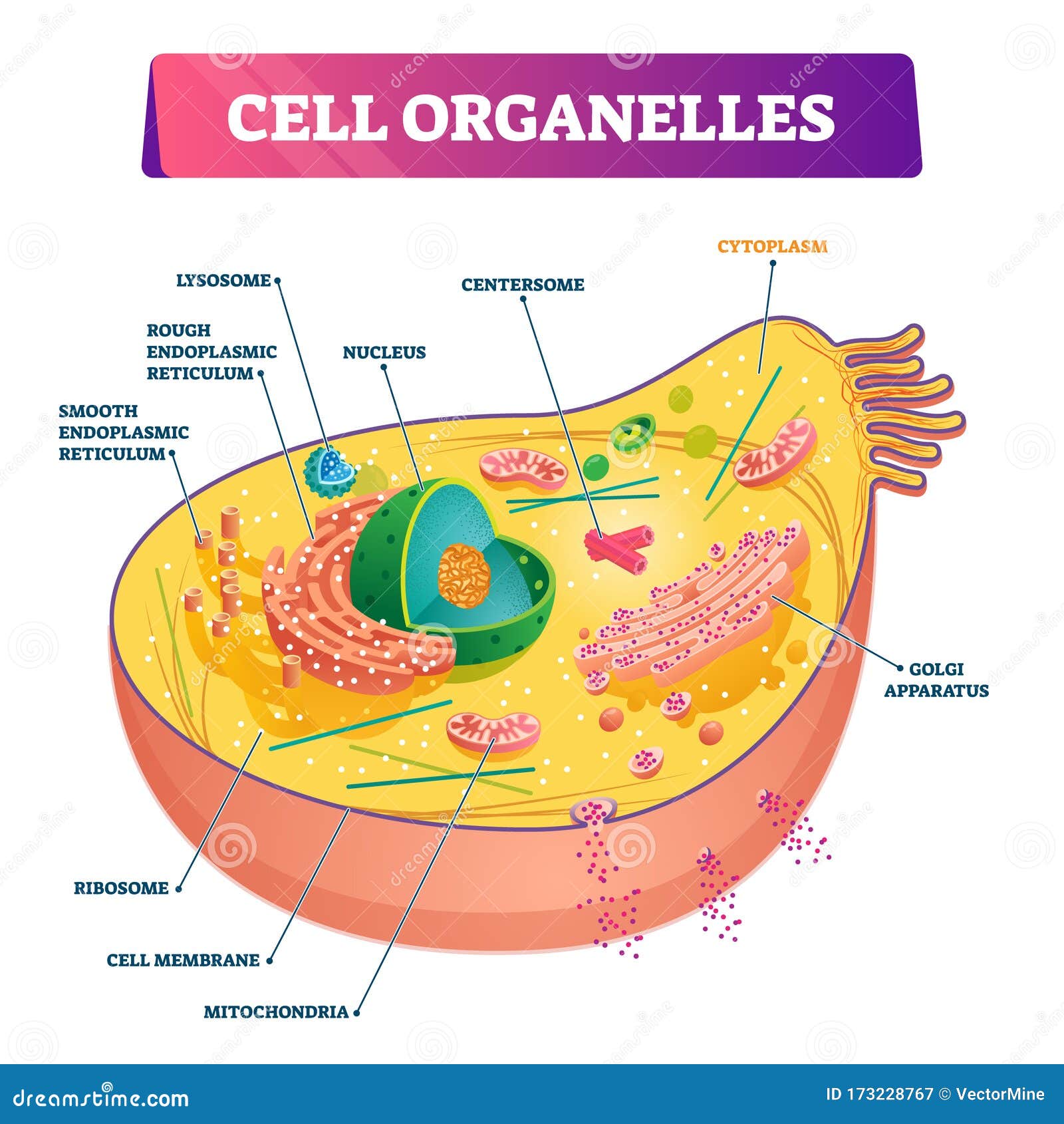
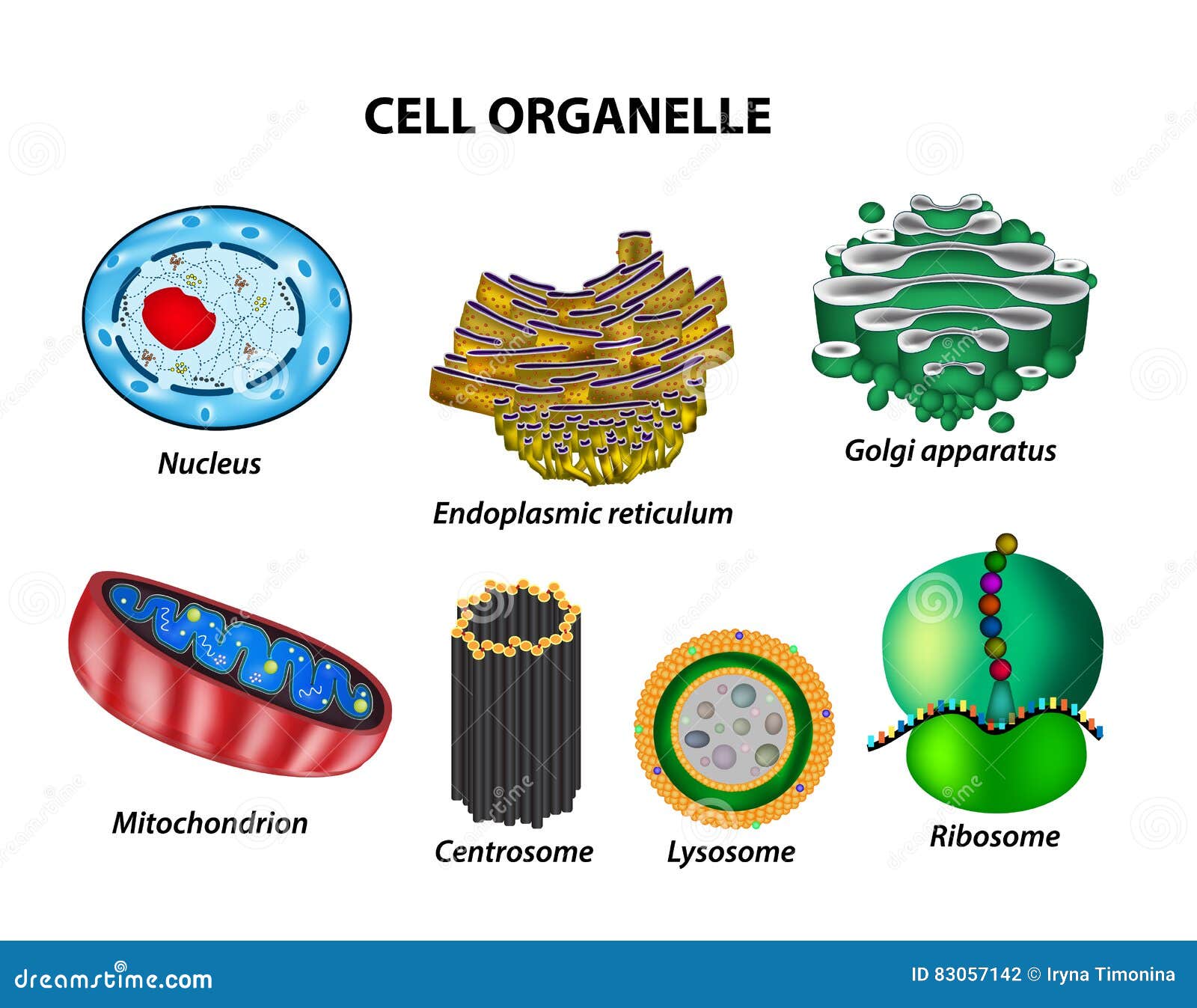
Nucleus Controls cell activities and contains genetic code Membrane-bound to prevent digestion of cell contents.Store digestive enzymes (digest food molecules, worn-out organelles, engulfed bacteria etc).Plant cells usually have one very large vacuole, animal cells have a number of small vacuoles.Controls turgidity (how full or limp the cell is).raw materials used in synthesis of proteins.Cell sap - concentrated solution of sugars, salt and suspended proteins.mucus in goblet cells Allows transport of materials.add carbohydrate component to glycoproteins.Golgi Bodies / apparatus Series of flattened hollow discs Packages proteins & lipids in pinched-off vesicles: Large surface area for ribosome attachment.Rough ER – has ribosomes for protein synthesis.Smooth ER - synthesis of lipids, including steroids, and calcium storage in muscles.connects with membrane system within cell Įndoplasmic reticulum Tube-like network from nucleus to membrane.Cell Organelles Cytoplasm – matrix of the cell Membrane system – includes endoplasmic reticulum & golgi bodies Organelles – self-contained, membrane-bound structures such as nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts Vesicles – membrane-bound bubbles of liquid, including vacuoles, lysosomes, secretory and transport vesiclesĬell (plasma) membrane Surrounds cytoplasm and organelles and controls entry/exit of all substances (semi-permeable)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
